First and foremost, I have to warn you that you will not like this article if you are not really into audio technology because this article contains many audio technology details that for people who aren’t audiophiles, might sound boring, but it is what it is, I can be funny, but not when it comes to specific scientific stuff!
In this article, I’m going to do something that I haven’t done in my previous articles.
I’m going to give a quick and short answer to the question right away and then I’ll expand my answer in more detail so you have more context on the question.
What Does 24bit 96 kHZ Mean ?
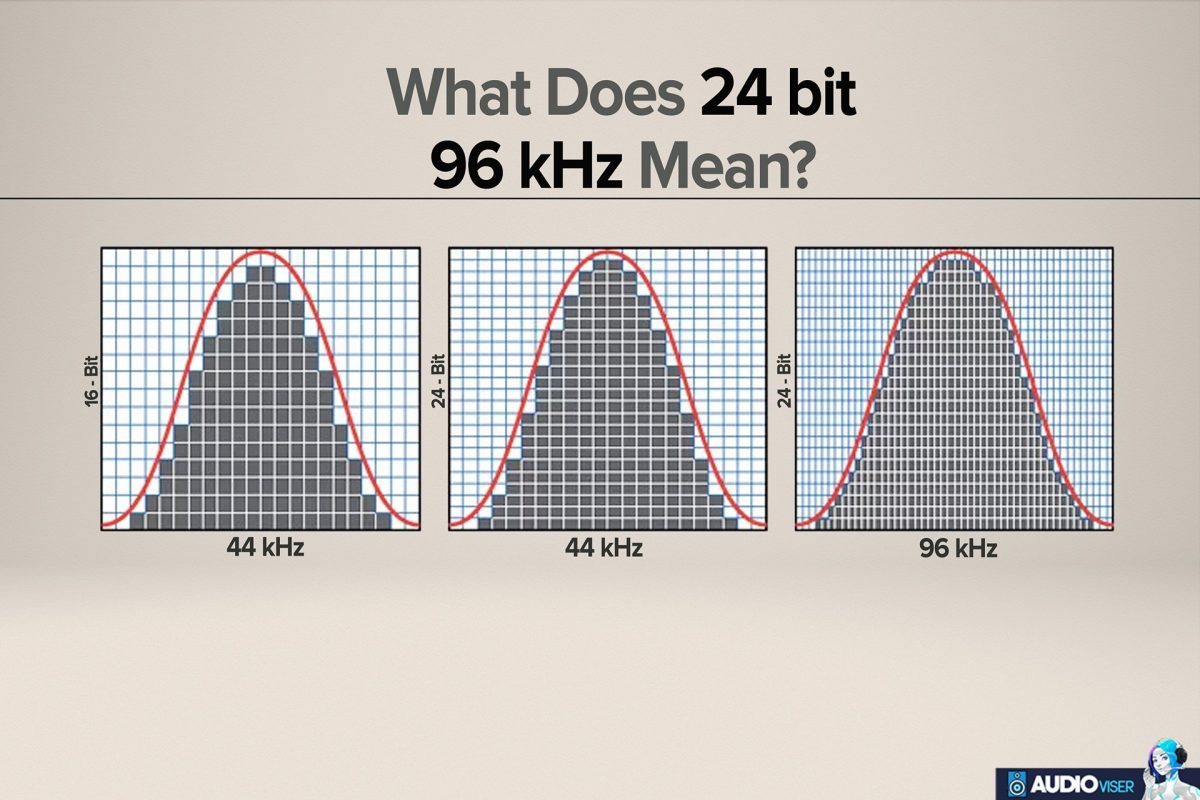
96kHz is referring to the sample rate of the audio, meaning there will be 96,000 samples per second. However, the 24bit depth does not refer to the volume. It actually refers to the size of the samples.
Sample Rate & Bit Depth
The combination of bit depth and sample rate determines the resolution of digital audio. Therefore, when you begin a new session in the majority of DAWs, including Pro Tools, you are prompted to set each of them.
While a recording’s sample rate determines its frequency content, its dynamic range is determined by bit depth.
Sample Rate
The rate at which samples are taken is known as the sampling rate. Imagine a track of analog audio. In the binary language of 1s and 0s, a “sample” is a measurement, a snapshot, at one particular point in that audio track.
Tens of thousands of times per second, repeat that measurement; the sample rate or sampling frequency is the number of times that snapshot is captured. It is expressed in kiloHertz (kHz), which is a unit that means 1,000 times per second, and is measured in “samples per second.”
For instance, the analog signal on an audio CD is sampled 44,100 times per second at a 44.1kHz sample rate.
The Nyquist-Shannon theorem, which was developed in the 1940s, is where sample rates’ scientific foundations lie. According to the theory, the original signal can be accurately recreated when the sampling frequency is larger than twice the maximum frequency of the signal being sampled.
The original analog signal can be recreated without any loss as long as the Nyquist limit, which is half the sample rate, exceeds the highest frequency of the signal being sampled. Lower sampling rates may not fully recover the source signal’s information from the sampled signal or may produce the audible artifact known as “aliasing.”
The highest frequency that can be recorded and stored at a sample rate of 44.1 kHz is just below half of that rate, or roughly 22 kHz. Though most of us do not detect frequencies that high in practice, the acknowledged range for the human hearing range is from 20 Hertz to 20,000 Hertz (or 20kHz).
Sensitivity to high frequencies is decreased with age, loud sound exposure, and environmental factors. The Nyquist frequency is well over an octave above the audible range when recording at 96kHz, whereas recording at 48kHz raises the Nyquist frequency to just under 24kHz.
What Does Sample Rate Do?

Even though many claim that sample rate measures or captures a lot of different activities, it actually just measures frequency. There you go.
How Is Sound Quality Impacted By Sample Rate?
How many sound samples, or measurements, are taken per second is known as the sampling rate. The audio quality improves when more samples are taken and more information about the locations where the waves rise and fall is captured. The sound wave’s form is also more precisely captured.
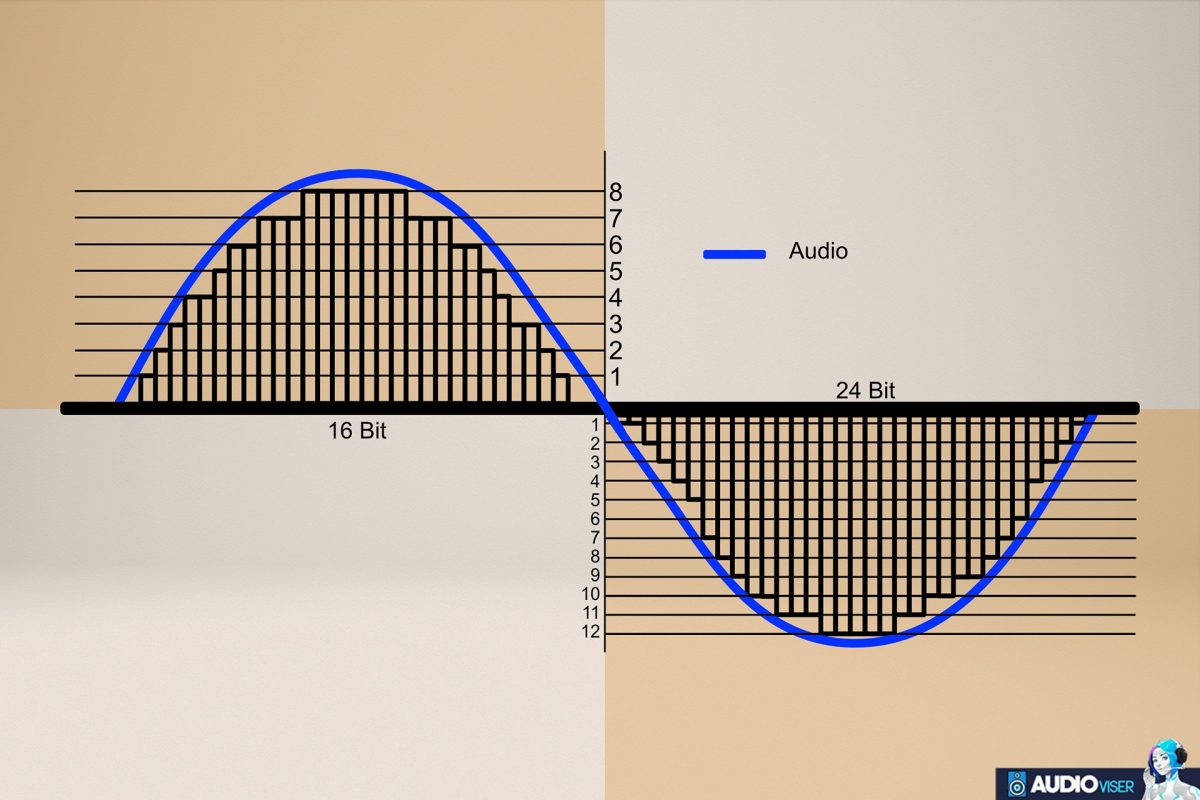
Bit Depth
The number of amplitude values that can be recorded for each sample depends on the audio bit depth. 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit audio bit depths are the most popular. Each term is binary and can have a variety of values. Systems with greater audio bit depths can express a wider range of possible values:
- 16-bit: 65,536 values
- 24-bit: 16,777,216 values
- 32-bit: 4,294,967,296 values
More amplitude values are available for us to record with a larger audio bit depth, which also translates to a higher resolution. As a result, when the continuous analog wave is sampled, its exact amplitude is closer to a value that is available. And as a result, a digital amplitude approximation gets closer to the actual fluid analog wave.
How Does Bit Depth Affect Sound Quality?
The higher the bit depth, the more data will be captured to more accurately re-create the sound. If the bit depth is too low, information will be lost, and the reproduced sample will be degraded. For perspective, each sample recorded at 16-bit resolution can contain any one of 65,536 unique values
Can the human ear hear the difference between audio bit depths?
You might be wondering if human ears can actually distinguish between amplitude levels between 65,536 and 4,294,967,296.
This is a legitimate inquiry. Even in a 16-bit machine, the noise level is remarkably low. 16-bit is a feasible option for a project’s final bounce, unless you require higher dynamic range than 96 dB.
However, using a larger audio bit depth when working on a project is not a bad idea. You essentially have greater headroom before distortion happens because the noise floor drops, which is also referred to as headroom. This additional buffer period before distortion offers greater flexibility and serves as a useful failsafe while working.
Final Words
If you are left confused after this article, let me just say that you are not the only one, I am confused, as well. I guess when it comes to audio technology, we should leave it to the experts and people who really understand such stuff.
Nevertheless, I still think that I did a good job writing this article, because at the end of the day, I answered the main question, and I made sure to include even more details.
Details that I can’t say I understand fully, but I do understand the core of it, and I think that is enough to be understood. If you want more details, you are free to grab the physics book, cause there you will find everything you need.
Further Reading
Audio interfaces are well known to be working with all the things that I just mentioned above. Check the best Audio Interfaces for Shure SM7B.
You can also check the best audio interfaces for FL studio.
Give a read to the article about the best audio interfaces for GarageBand.
Voice over audio interfaces are also an important part of the audio equipment, so you can read all about them here.
Audio Engineer
You’ll never find anyone more passionate about audio as me. I love to share my knowledge with others and help people find the right equipment for them.





